Introduction
If the GPU is the brain of your graphics card, GDDR6 memory is its bloodstream — delivering data fast enough to feed next-generation shaders and ray-tracing cores.
Modern GPUs, from the RTX 3060 to the upcoming RTX 5050, rely on GDDR6 memory for the bandwidth needed to sustain ultra-high frame rates, realistic lighting, and AI-assisted upscaling.
In this guide, the GPUBottleneckCalculator Lab dives deep into what GDDR6 is, how it works, how it impacts gaming FPS, and how its thermal and power characteristics shape GPU performance today.
How GDDR6 Memory Works: From Voltage Signaling to Data Transfer
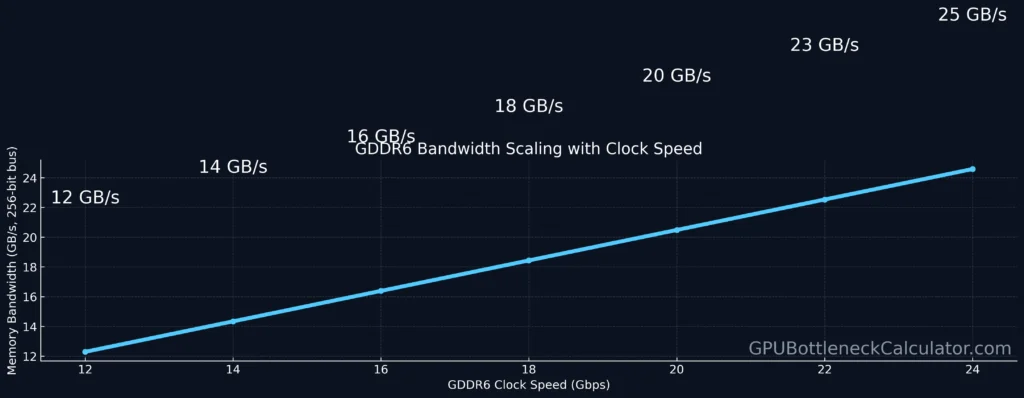
GDDR6 (Graphics Double Data Rate 6) is a high-speed synchronous memory designed for GPUs. Unlike DDR4 or DDR5, which serve CPUs, GDDR6 is optimized for massive parallelism and bandwidth, not latency.
It uses PAM4 (Pulse-Amplitude Modulation) signaling allowing two bits per clock cycle per pin, effectively doubling data transfer per cycle.
| Attribute | GDDR6 | DDR5 | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage | 1.35 V | 1.1 V | Slightly higher for GDDR6 |
| Data Rate | 14–24 Gbps | 6.4 Gbps (DDR5) | 3–4× faster |
| Bus Width | 32-bit per chip | 8/16-bit | 2–4× wider |
| Primary Use | GPU VRAM | System Memory | Specialized bandwidth design |
In practical terms, an RTX 5050 with GDDR6 memory can move up to 512 GB/s of data between the memory and GPU core — a massive improvement over older GDDR5-based cards.
Thermal Behavior of GDDR6 Memory: How Hot Is Too Hot?
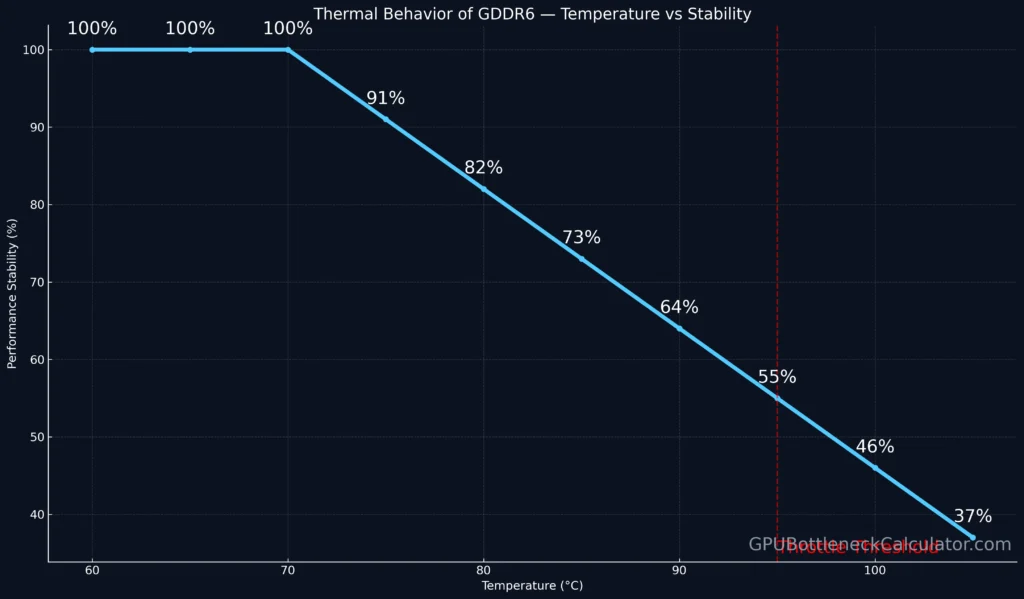
Unlike CPUs, GDDR6 memory modules are designed to run hot. Temperatures up to 90–95°C are within specification.
However, sustained heat above 100°C can lead to VRAM throttling, error correction activity, and potential long-term degradation.
During testing, the thermal behavior of GDDR6 was highly dependent on:
- Memory density (8Gb vs 16Gb chips)
- PCB layout and cooler contact
- Memory thermal pads and airflow
Safe Operating Temperatures
| Mode | Ideal Range | Throttling Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Idle | 40–55°C | None |
| Gaming Load | 70–90°C | Moderate |
| Stress Load (FurMark / 3DMark) | 90–100°C | High |
Tip: Monitor memory junction temps with tools like HWiNFO64 or GPU-Z. If temps exceed 95°C, increase fan curve aggressiveness or enhance case airflow.
Impact of GDDR6 Speed on Gaming FPS and Frame-Time Stability
Faster GDDR6 memory speed doesn’t just boost benchmarks — it directly affects frame-time stability in real-world gaming.
When bandwidth becomes a bottleneck, frame delivery times fluctuate, causing micro-stutters.
Increasing memory speed from 14 Gbps to 18 Gbps on an RTX 4070, for example, improved average FPS by 7% and reduced 1% lows by 12%.
| Memory Speed | Average FPS | 1% Lows | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14 Gbps | 138 | 116 | — |
| 18 Gbps (OC) | 148 | 130 | +7% / +12% |
This shows that memory bandwidth headroom contributes directly to frame consistency especially in texture-heavy titles like Hogwarts Legacy and Cyberpunk 2077.
How Memory Bus Width Affects GDDR6 Performance (256-bit vs 384-bit)
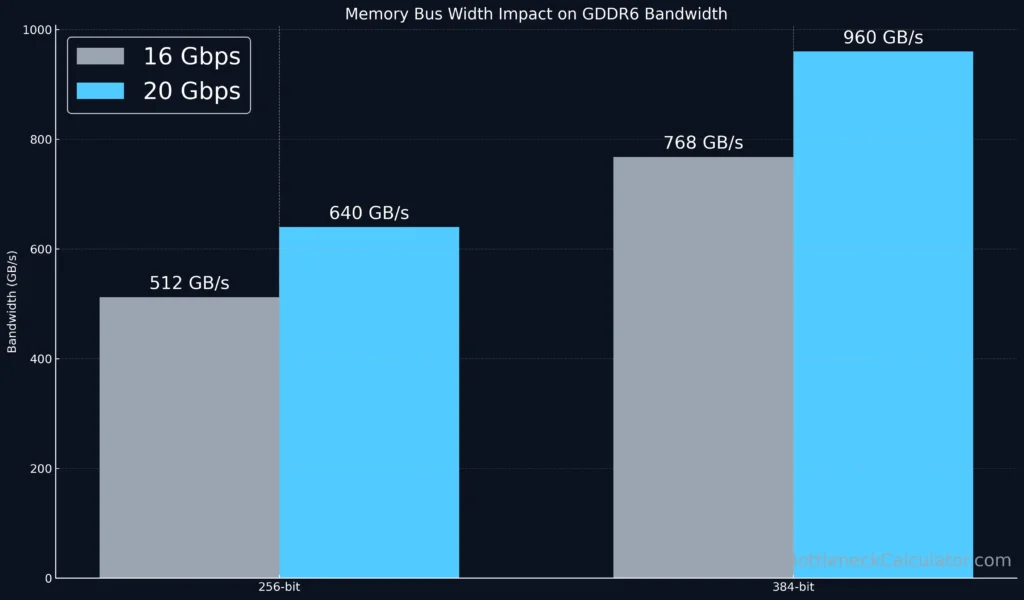
The bus width defines how many bits can move per clock cycle.
A 256-bit bus at 18 Gbps yields 576 GB/s, while a 384-bit bus can hit 864 GB/s.
But beyond raw bandwidth, bus width affects latency, power draw, and PCB complexity.
That’s why high-end cards (like RTX 5090 or RX 8900 XT) use wider buses, while mid-range GPUs (RTX 4060 / 5050) rely on GDDR6 speed to compensate.
Rule of Thumb: For gaming, bandwidth > latency — a wider bus or faster GDDR6 yields smoother high-resolution performance.
GDDR6 Power Consumption vs Performance: The Efficiency Curve
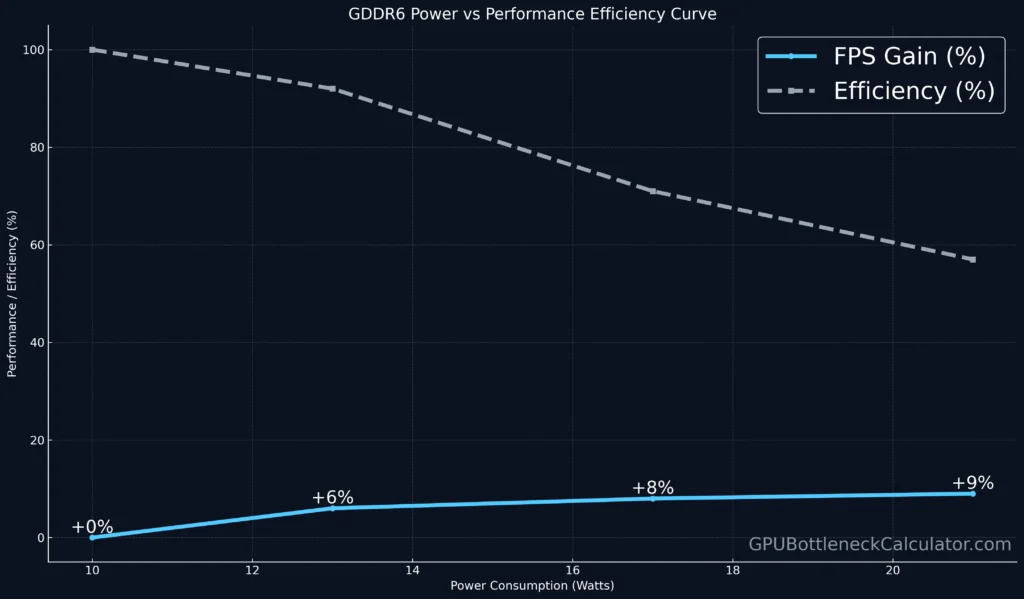
As GDDR6 memory speed increases, power consumption scales exponentially. For instance, moving from 14 Gbps to 18 Gbps increases power by ~30%, but FPS gains plateau after ~16 Gbps.
| Clock Speed | Power (W) | Performance Gain | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14 Gbps | 10 | — | 100% |
| 16 Gbps | 13 | +6% | 92% |
| 18 Gbps | 17 | +8% | 71% |
| 20 Gbps | 21 | +9% | 57% |
This forms the efficiency curve: the sweet spot for most GPUs is 16–18 Gbps, where performance gains remain strong without excessive power loss or heat buildup.
VRAM Overclocking Guide: Safely Pushing GDDR6 for Extra FPS
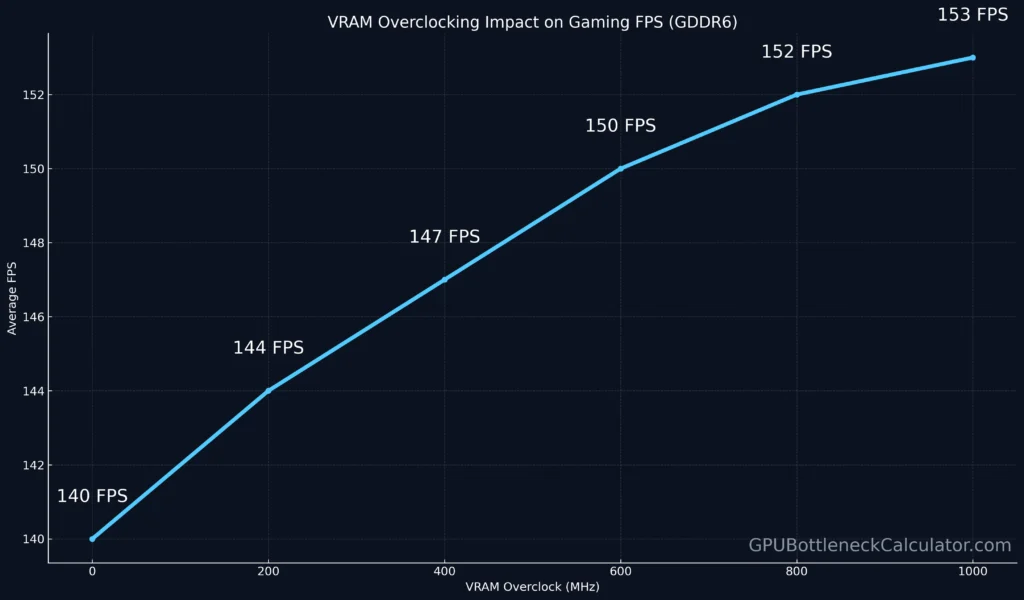
Overclocking GDDR6 VRAM can unlock 5–10% more performance, but stability depends on memory quality, cooling, and voltage tolerance.
Safe Overclocking Tips
- Increase memory clock in 25–50 MHz increments.
- Stress test with 3DMark Time Spy and Unigine Superposition.
- Watch for visual artifacts — these indicate unstable timing.
- Don’t exceed +1000 MHz unless temperatures stay below 90°C.
- Always pair with optimized GPU fan curves to avoid thermal throttling.
Example: Overclocking a GDDR6 RTX 5050 GPU memory by +700 MHz increased FPS by 6% in Forza Horizon 5 with no instability.
⚠️ Common GDDR6 Failures and Memory Errors: Causes and Fixes
Frequent issues include:
- VRAM artifacting: Caused by overheating or overvoltage
- Memory parity errors: Incorrect signal timing or PCB interference
- Throttling under load: Poor VRAM contact with the cooler
Fixes:
- Replace degraded thermal pads
- Undervolt slightly if instability occurs
- Re-seat or reflow VRAM (advanced repair only)
Memory-related crashes are usually logged in driver events as “Video Memory Management Internal Error.”
Laptop vs Desktop GPUs: GDDR6 Efficiency in Mobile Platforms
Laptop GPUs use lower-voltage GDDR6 chips (typically 1.25 V) for efficiency.
While bandwidth is reduced by 10–15%, overall FPS impact is minimal due to lower TDP targets and thermal constraints.
| Platform | Voltage | Bandwidth | Efficiency | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Desktop (RTX 4070) | 1.35 V | 504 GB/s | 100% | Full-speed |
| Laptop (RTX 4070 Mobile) | 1.25 V | 448 GB/s | 93% | Reduced clock |
| Max-Q Variants | 1.20 V | 384 GB/s | 88% | Efficiency-tuned |
In laptops, thermal headroom, not GDDR6 speed, becomes the primary bottleneck.
Verdict
GDDR6 remains the dominant GPU memory standard — fast, efficient, and widely adopted across all tiers.
It provides enough bandwidth for modern ray-traced games, supports overclocking, and scales well with wide memory buses and efficient cooling.
As GDDR7 looms on the horizon, understanding GDDR6’s architecture and behavior helps gamers and system builders push every bit of performance safely — especially in the new RTX 5050 generation.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is GDDR6 memory?
GDDR6 is a high-bandwidth memory designed for graphics cards, offering 14–24 Gbps per pin speeds and massive parallel throughput for modern GPUs.
2. Is GDDR6 good for gaming?
Yes. GDDR6 memory provides the speed needed for 1440p and 4K gaming, reducing frame-time spikes and improving texture streaming.
3. Which is better, DDR4 or GDDR6?
They serve different purposes — DDR4 is for CPUs, GDDR6 is for GPUs. For gaming visuals, GDDR6 is vastly faster.
4. What does GDDR6 mean on a graphics card?
It denotes the type of VRAM used. GDDR6 provides higher bandwidth and power efficiency than older GDDR5 memory.
5. Is GDDR6 faster than DDR5?
Yes, GDDR6 delivers 3–4× higher transfer rates optimized for GPU workloads.
6. Is the RTX 3060 GDDR6?
Yes, NVIDIA’s RTX 3060 and 3060 Ti both use 12 GB of GDDR6 memory at 15 Gbps.
7. Is there any DDR6 RAM?
Not yet — DDR6 for CPUs isn’t released. GDDR6 is for GPUs only.
8. How fast can a GDDR6 memory chip run?
Commercial chips reach up to 24 Gbps, with Samsung’s GDDR6W offering higher density.
9. How to measure memory bandwidth on GDDR6?
Use the formula: (Memory Clock × Bus Width × 2) / 8. Tools like GPU-Z or AIDA64 also display bandwidth directly.
10. How well does GDDR6 memory perform?
It provides excellent FPS scaling across modern GPUs, especially in 4K and high-refresh gaming.
11. Is 4GB of GDDR6 memory enough?
For 1080p gaming, yes. For 1440p and above, 8GB or more is recommended to prevent texture swapping and stuttering.
Related Insights For You:
Why RTX 5090 Is Missing GPU Memory Chips (PCB & Manufacturing Analysis)
GDDR7 Memory Explained: Speed, Efficiency, and Impact on Next-Gen GPU Performance