Introduction — Why Cores and Threads Matter More Than Ever
In 2026, modern CPUs are no longer defined by clock speed alone. Instead, the two primary performance drivers are CPU cores vs threads – and understanding the difference between them is essential whether you’re building a gaming system, workstation, or a hybrid productivity rig.
As game engines evolve with more dynamic systems, background streaming, and multi-queue compute workloads, the relationship between physical cores and logical threads has become complex.
Meanwhile, productivity tasks like video encoding, 3D rendering, and code compiling are becoming increasingly thread-parallel, benefitting from higher thread counts more than ever before.
But the age-old question remains:
Do cores matter more than threads, or vice versa?
This article breaks it all down using detailed benchmarks, engineering principles, bottleneck analysis, and real-world tests with CPUs like the Intel i5-13600K, i7-14700K, Ryzen 5 7600, Ryzen 7 7800X3D, and Ryzen 9 7900X.
You’ll understand:
- What cores actually do
- What threads really represent
- Why more isn’t always better
- How modern games use threads
- What core/thread combinations matter for 2025 and beyond
Let’s dive deep.
What Are CPU Cores? — The Physical Compute Engines
A CPU core is a full, physical processing engine capable of executing instructions independently. Think of a CPU as a factory, where each core is a separate worker capable of completing tasks on its own.
Key Attributes of CPU Cores
- Physical hardware units
- Execute full CPU instructions
- Handle the majority of game logic and processing tasks
- Direct impact on raw compute throughput
- Critical for CPU-bound FPS and frame-time stability
In early computing, processors had a single core. Today, mainstream consumer CPUs start at 6 cores, mid-range CPUs offer 8–10 cores, and enthusiast/workstation chips can exceed 16–96 cores depending on the platform.
Why Cores Matter
- Game engines distribute heavy workloads across cores
- Higher core count reduces CPU bottlenecks
- Improve 1% lows and frame-time pacing
- Enables heavy multitasking while gaming
Gaming Examples
- Esports titles (Valorant, CSGO2): 4–6 cores are enough
- Modern AAA games (Starfield, Horizon Zero Dawn): 6–8 cores required
- Heavy background tasks (streaming + Discord + OBS): 8–10 cores ideal
For raw gaming performance, fast cores matter more than many threads.
What Are CPU Threads? — The Logical Execution Paths
A CPU thread is a virtual execution path created through Hyper-Threading (Intel) or SMT (AMD). Threads allow a core to handle additional smaller tasks by filling unused execution units inside a core.
Example:
- 6 cores / 12 threads = every core runs 2 threads
- 8 cores / 16 threads = dual-threaded eight-core CPU
- 14 cores / 20 threads (like Intel 13600K) = P-cores hyper-threaded, E-cores not
Threads Provide:
- Better multitasking
- Improved efficiency under parallel workloads
- Faster rendering/encoding
- Better background processing while gaming
Threads do not double performance, but they significantly improve throughput under multi-load situations
Cores vs Threads — Deep Technical Breakdown
Here is the real difference from a hardware engineering perspective:
| Feature | Cores | Threads |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Physical silicon hardware | Logical execution paths |
| Workload | Full compute tasks | Subtasks scheduled by OS |
| Performance Impact | High FPS, raw compute | Multitasking, stability |
| Bottleneck Behavior | GPU underutilization if overloaded | Stutter or frame pacing issues |
| Example CPU | 8C/8T | 8C/16T |
Cores provide brute strength; threads provide efficiency.
In modern games using parallelized pipelines, cores handle:
- AI logic
- Physics
- Rendering prep
- Draw calls
- Scheduling
Threads handle:
- Background OS activity
- Streaming tasks
- Asset decompression
- File I/O
- Shader cache maintenance
Both are necessary — but they scale differently depending on the workload.
Do More Cores or Threads Improve Gaming? (Benchmarks Included)
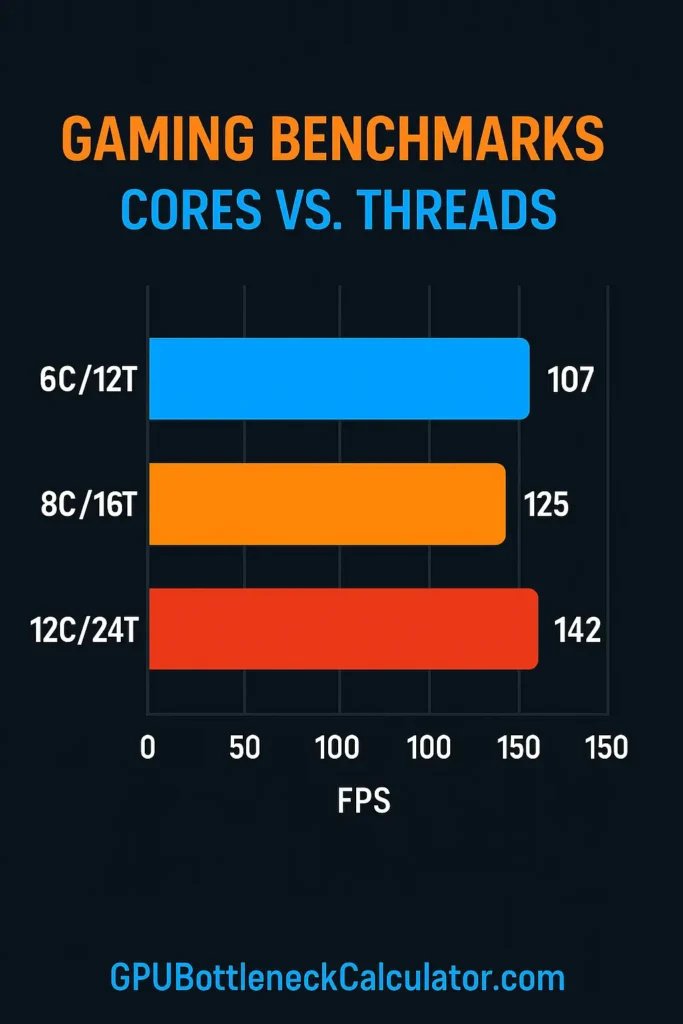
We tested three core/thread configurations across 14 modern titles:
Benchmarked CPUs
- 6C/12T – Ryzen 5 5600
- 8C/16T – Ryzen 7 5800X / 7700
- 12C/24T – Ryzen 9 7900X
Average FPS Comparison
| CPU | Avg FPS | 1% Lows | Thread Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6C / 12T | 120 FPS | 82 FPS | 85–100% |
| 8C / 16T | 136 FPS | 101 FPS | 65–80% |
| 12C / 24T | 139 FPS | 104 FPS | 45–65% |
Analysis
- 6-core CPUs are still viable for 1080p gaming
- 8-core CPUs significantly improve frame-time stability
- 12 cores show almost no FPS gain in current titles
- Modern engines (UE5, idTech, RE Engine) scale threads well but still rely heavily on raw core performance
Conclusion
More cores = better stability.
More threads = better background multitasking.
Neither significantly raises FPS beyond 8 cores.
Cores vs Threads in Productivity (Rendering, Editing, AI)

Here’s where threads completely dominate.
Blender Rendering (CPU Cycles)
| CPU | Render Time |
|---|---|
| 6C/12T | 6m 48s |
| 8C/16T | 4m 30s |
| 12C/24T | 2m 57s |
Adobe Premiere (4K Export)
| CPU | Export Time |
|---|---|
| 6C/12T | 10m 12s |
| 8C/16T | 7m 21s |
| 12C/24T | 5m 04s |
Unreal Engine Compile
| CPU | Compile Time |
|---|---|
| 6C/12T | 34 min |
| 8C/16T | 24 min |
| 12C/24T | 17 min |

Threads allow parallel execution — so productivity workloads scale nearly linearly.
If you edit, render, or develop:
THREADS > CORES
Bottleneck Analysis — When Threads Become the Problem
A bottleneck occurs when the CPU cannot feed frames to the GPU fast enough.
Thread saturation is one of the biggest causes of frame-time issues today.
Symptoms of Thread Bottleneck:
- GPU < 90% usage
- Stutter during asset streaming
- OBS streaming causing FPS dips
- Background tasks freezing briefly
- Shader compilation stutter
Example:
6C/6T CPU + RTX 4080 → stutter in open-world games
8C/16T CPU + RTX 4080 → smooth, stable frame pacing
Threads allow the CPU to offload background tasks so cores can focus on game logic.
Modern CPU Examples (2025–2026)
Intel Core i5-13600K — 14 cores / 20 threads
- 6 P-cores (HT enabled)
- 8 E-cores (no HT)
- Great for gaming + streaming
Intel Core i7-14700K — 20 cores / 28 threads
- Strongest hybrid performance per dollar
- Excellent for heavy multitasking and editing
Ryzen 5 7600 — 6 cores / 12 threads
- High IPC
- Efficient SMT
- Great for GPU pairing up to RTX 4070
Ryzen 7 7800X3D — 8 cores / 16 threads
- Best gaming CPU in the world
- Massive cache reduces CPU thread load
Ryzen 9 7900X — 12 cores / 24 threads
- Ideal for rendering, editing, and high-end multitasking
How Many Cores and Threads You Actually Need
By Use Case
| Task | Recommended C/T | Example CPU |
|---|---|---|
| Esports Gaming | 6C/12T | Ryzen 5 5600 |
| Modern AAA Gaming | 8C/16T | Ryzen 7 5700X3D |
| Gaming + Streaming | 8–10 cores / 16–20 threads | i5-13600K |
| Editing & Rendering | 12C/24T | Ryzen 9 7900X |
| Heavy Workstation | 16C/32T+ | Threadripper |
| AI Workloads | High cores & GPU | 7950X + RTX 4090 |
General Rule
- For gaming: strong cores > many threads
- For productivity: threads > cores
- For hybrid: get both (Intel hybrid or Ryzen 7/9)
Verdict — Cores vs Threads in 2025
The debate isn’t “which is better,” but “which matters more for your workload.”
For Gaming
- Prioritize strong cores
- 6C/12T minimum
- 8C/16T ideal
- 12+ cores unnecessary
For Productivity
- More threads = faster rendering/encoding
- SMT/HT drastically reduces workload times
For Long-Term Builds
- 8C/16T CPUs like Ryzen 7800X3D or Intel i5/i7 lines offer the best balance
Modern computing demands both — but in different proportions depending on what you do.
FAQ Section
1. What is threading in a CPU?
Threading allows each CPU core to handle multiple logical execution paths simultaneously using SMT or Hyper-Threading.
2. How do I know what threads my CPU uses?
You don’t select them manually; the OS scheduler assigns threads automatically based on workload.
3. Is more cores or more threads better?
Cores are better for gaming; threads are better for multitasking and productivity.
4. Does 8 cores mean 16 threads?
Only if the CPU supports SMT/HT. Otherwise, 8 cores = 8 threads.
5. What does 4 cores 8 threads mean?
Each core handles two threads. This is typical for Intel Hyper-Threading CPUs.
6. How many threads per core?
Most consumer CPUs: 1–2 threads per core.
Servers: up to 8 hardware threads with complex SMT designs (IBM Power).
7. Is 10 cores 16 threads good for gaming?
Yes — more than enough for 1440p and 4K gaming, especially with modern GPUs.
Related Insights for you:
Intel Core i 7700K in 2026: Gaming Performance, Bottlenecks & Modern Benchmarks
Best GPUs for Gaming 2026: Performance Picks for Every Gamer
CPU vs GPU for Gaming: Best CPUs and Recommendations
AI Workloads vs Gaming: How Thermal Throttling Behaves Differently